- Ovirt Windows Network Driver
- Ovirt Windows Disk Drivers
- Ovirt Version
- Ovirt Driver Download
- Ovirt Windows Drivers
- Ovirt Drbd
OVirt is an open-source distributed virtualization solution, designed to manage your entire enterprise infrastructure. OVirt uses the trusted KVM hypervisor and is built upon several other community projects, including libvirt, Gluster, PatternFly, and Ansible. OVirt 4.3 features and bug fixes: Improved performance when running Windows as a guest OS. Included with this release are the latest Oracle VirtIO Drivers for Microsoft Windows. Higher level of security with TLSv1 and TLSv1.1 protocols now disabled for vdsm communications.
For production installations, we recommend installing oVirt using the graphical Cockpit installer in theSelf-Hosted Engine configuration. In this configuration, oVirt Engine and a Host are installedtogether with the Engine running as a Virtual Machine on that Host. This configuration ispreferred because the Engine Virtual Machine will be highly available (once a second Host is added).
However, if you prefer to run oVirt Engine standalone on physical hardware or another virtualization provider, you can install oVirt Engineand Nodes / Hosts separately.
oVirt 4.4.4 is intended for production use and is available for the following platforms:
Engine:
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.3
- CentOS Linux 8.3
- CentOS Stream (Tech Preview)
Hosts:
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.3
- CentOS Linux 8.3
- oVirt Node (based on CentOS Linux 8.3)
- CentOS Stream (Tech Preview)
See the Release Notes for oVirt 4.4.4.
Install oVirt Engine using RPM
oVirt Engine is installed using RPM packages on a supported Enterprise Linux 8 distribution,such as CentOS Linux or Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
Users can also compile from source, using the guides found under the Developers section. This is not recommendedunless you are a developer or need to customize the source code.
Important: Ratio entwicklungen driver download for windows 10 32 bit. You cannot skip a version when updating oVirt Engine. For example, if you are updating from3.6 to 4.4, you first need to update to 4.0, then to 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 and finally to 4.4. (Host upgrades can use theoVirt Fast Forward Upgrade tool.)If you are updating from 4.3, please note you’ll need to migrate your engine from el7 to el8.
Upgrading from previous releases
For a standalone engine this means basically:
- backup engine data on 4.3.10 with:
engine-backup --scope=all --mode=backup --file=backup.bck --log=backuplog.log - copy the backup to a safe location
- reinstall engine host with EL 8
- enable repos with:
dnf install https://resources.ovirt.org/pub/yum-repo/ovirt-release44.rpm dnf update(reboot if needed)- enable modules with:
dnf module enable -y javapackages-tools pki-deps postgresql:12 389-ds - install engine rpms with:
dnf install ovirt-engine - restore the engine data with:
engine-backup --mode=restore --file=backup.bck --log=restore.log --provision-db --provision-dwh-db --restore-permissions --provision-dwh-db - run
engine-setup.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux, CentOS Linux
Enable the Base, Optional, and Extra repositories (Red Hat Enterprise Linux only):
Add the official oVirt repository.
Install oVirt Engine.
Set up oVirt Engine.
Follow the prompts to configure and install the Engine.
Once the installation completes, oVirt’s web UI management interface will start and the URL will be printedto the screen. Browse to this URL to begin using oVirt!
See Browsers and Mobile Clients for supported browsers andmobile client information.
Download oVirt Node or Setup Hosts
You must now install at least one Node or Host to act as hypervisors. Enterprise features like migration and high availabilityrequire more than one Host.
oVirt supports two types of Hosts:
- oVirt Node and
Depending on your environment requirements, you may want to use only oVirt Nodes, only EL Hosts, or both.
Download oVirt Node
oVirt Node is a minimal operating system based on CentOS that is designed to provide a simple method for setting up aphysical machine to act as a hypervisor in an oVirt environment.
Download the oVirt Node Installation ISO (current stable is oVirt Node 4.4 - Stable Release - Installation ISO)
Write the oVirt Node Installation ISO disk image to a USB, CD, or DVD.
Boot your physical machine from that media and install oVirt Node.
Or Setup a Host
Instead of or in addition to oVirt Node, you can use a standard Enterprise Linux installation as a Host.
An Enterprise Linux Host (such as CentOS or RHEL), also known as an EL-based hypervisor or EL-based Host, is a standardbasic installation of an Enterprise Linux operating system on a physical server upon which the hypervisorpackages are installed.
Install one of the supported operating systems (CentOS, RHEL) on your Host and update it:
Add the official oVirt repository:
See Chapter 7: Enterprise Linux Hosts for full installationinstructions.
Attaching your Hosts
Once you have installed additional oVirt Nodes or EL Hosts, use the oVirt Administration Portal to add them to the Engine.Navigate to Compute → Hosts → New and enter the Host details. SeeAdding a Host to the oVirt Engine for detailed instructions.
Storage
oVirt uses a centralized storage system for Virtual Machine disk images, ISO files, and snapshots. Before you can install a Virtual Machine,storage must be attached.
Storage can be implemented using:
Network File System (NFS)
GlusterFS exports
iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface)
Local storage attached directly to the virtualization Hosts
Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP)
Parallel NFS (pNFS)
Other POSIX compliant file systems
Using the oVirt Administration Portal, navigate to Storage → Domains → New and enter the Storage details.See Configuring Storage andStorage Administration for guidance on configuring storage for yourenvironment.
Install Virtual Machines
Once oVirt Engine is installed and you have added Hosts and configured storage,you can now install Virtual Machines!
See the Virtual Machine Management Guide for completeinstructions.
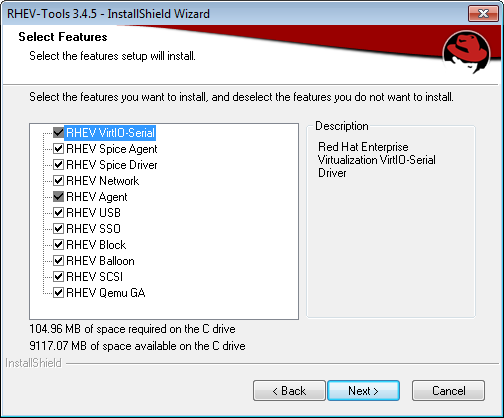
For best Virtual Machine performance and accurate dashboard statistics, be sure to install theoVirt Guest Agent and Drivers for Linux[for Windows]in each Virtual Machine.
The following virtual machine guest operating systems are supported:

| Operating System | Architecture | SPICE support [1] |
|---|---|---|
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3 - 6 | 32-bit, 64-bit | Yes |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7+ | 64-bit | Yes |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10+ [2] | 32-bit, 64-bit | No |
| Ubuntu 12.04 (Precise Pangolin LTS)+ [3] | 32-bit, 64-bit | Yes |
| Windows XP Service Pack 3 and newer | 32-bit | Yes |
| Windows 7 | 32-bit, 64-bit | Yes |
| Windows 8 | 32-bit, 64-bit | No |
| Windows 10 | 64-bit | Yes |
| Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2 and newer | 32-bit, 64-bit | Yes |
| Windows Server 2008 | 32-bit, 64-bit | Yes |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 64-bit | Yes |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 64-bit | No |
| Windows Server 2016 | 64-bit | No |
[1] SPICE drivers (QXL) are not supplied by Red Hat. Distribution’s vendor may provide SPICE drivers.
[2] select Other Linux for the guest type in the user interface
[3] not tested recently (?)
Consoles
The console is a graphical window that allows you to view and interact with the screen of a Virtual Machine.In oVirt, you can use a web-based console viewer or a desktop application (we recommend Remote Viewer).For Windows virtual machines, Remote Desktop Protocol is also available. See Installing Console Components,VNC Console Options, andand Browser Support and Mobile Clients for more information.
RPM Repositories and GPG keys
See RPMs and GPG for older releases, nightlies, mirrors, and GPG keys.
13 Sep 2017Introduction
In oVirt 4.1.4, we added a new feature called vGPU passthrough. vGPU is a technology that allows us to “shard” a physical GPU (GRID capable, like NVIDIA Tesla M60) into number of smaller instances. Each instance can then be assigned to a VM, giving us the ability to run GPU-accelerated workloads. There is quite a bit of setup required to get the vGPU instance into the VM, and this is where oVirt comes to picture: it requires one time (per hypervisor and per VM) setup, but after that the vGPU creation and deletion is happening seamlessly. This post serves as a step-by-step guide to getting the vGPU feature up and running.
Step 1: Host Requirements
As far as hardware goes, the essential requirement is having a hardware that has IOMMU. The IOMMU must also be enabled – follow the steps in an older post. The second requirement is having vGPU capable GPU – please refer to NVIDIA datasheet. The indicator whether IOMMU is enabled can be seen in oVirt engine:
Update: IOMMU is not needed, vGPU should work even if “Device Passthrough” in the screenshot below is disabled.

Special requirement is the software - vGPU capable drivers must be installed on each host to be used for vGPU. Search for these at the NVIDIA site, download and install it according to instructions.
Additionally, each vGPU host needs a hook called vdsm-hook-vfio-mdev. The hook is available in oVirt repositories, making the installation as easy as typing
It should then be visible in oVirt engine, under Hosts -> Host Hooks section.
Ovirt Windows Network Driver
Step 2: Guest Requirements
Step 2.0: OS Choice
The drivers available for guest OS must support vGPU. Consult the documentation of the guest operating system and/or NVIDIA driver to see whether vGPU drivers are available and support the chosen OS.
Step 2.1: Installation
Install the guest OS without the vGPU being present. Spice or VNC should work without flaws to get us through the installation.
Step 2.2: Adding vGPU and installing drivers
After the guest OS is installed, shut down the VM. We can now add the vGPU instance, but keep in mind that it will not be fully functional until the corresponding guest OS vGPU driver is installed. The process for adding a vGPU instance is as follows:
First, we have to figure out a vGPU instance type to use. That information is provided by NVIDIA datasheets, or we could SSH to one of the hypervisors where the guest is expected to run and list available vGPU instances:
The mdev keys (nvidia-11, nvidia-12, …) are so called mdev instance types. We need to note the name of the desired type. Its attributes indicate how many of these instances can be present at once, and the type’s properties. Please note that right now, each reported GPU (warning: Tesla M60 contains 2 GPUs, verify how many actual GPUs are present via lspci or Host Devices within oVirt engine) may only spawn homogeneous (aka same) instances.
Then we enter the value as custom property for the desired VM:

Ovirt Windows Disk Drivers
As vGPU does not have a graphical output, Spice/VNC should still be used as a primary way to interact with the OS (with GUI). It is also possible to use serial console (oVirt has one built-in) or any other means of remote access. After system boots up, install the corresponding vGPU driver by following the instructions of NVIDIA’s installer. Reboot the guest after driver installation and verify that the vGPU is recognized:
Ovirt Version
Summary
And that’s it! Following these steps, we have a VM that has a vGPU. To verify the functionality, it may be a good idea to run software capable of taking advantage of the vGPU and see whether the performance meets the requirements.
Ovirt Driver Download
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.Ovirt Windows Drivers
Ovirt Drbd
Related Posts

Comments are closed.